Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing can be detected by any person or healthcare professional- through observation of signs and symptoms that appear during meals, or through validated questionnaires for symptom screening. Dysphagia can be painful and in some cases, swallowing is impossible. However, for a definitive diagnosis, it is important to first consult a doctor. The doctor may perform tests or refer you to a speech therapist for detailed assessment and treatment.
Among the validated questionnaires to discriminate or screen for swallowing disorders, the EAT-10 questionnaire is an Eating Assessment Tool, prepared by Dr. Belafsky under the patronage of Nestlé Health Science. This test allows for the evaluation of specific symptoms of dysphagia, to obtain a direct score. If the total score obtained is greater than or equal to 3, the person may have trouble swallowing effectively and safely and should be evaluated more thoroughly.
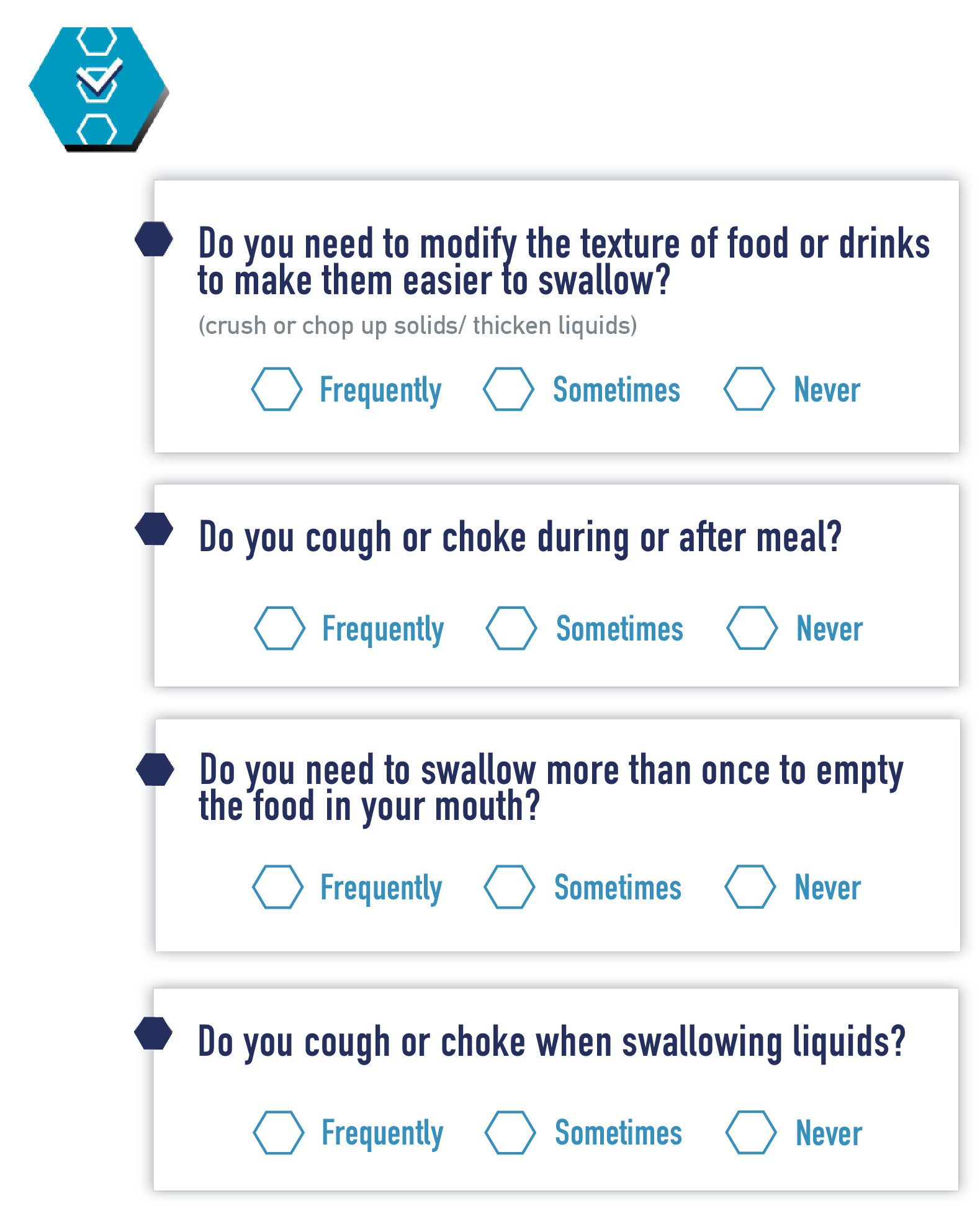
Information provided by the patient, their relatives or caregivers helps the healthcare professional to obtain as much data as possible to form a clinical judgment for the diagnosis.

Speech therapists are trained to help people with all kinds of oral conditions. We recommend consulting a speech therapist for diagnosis and treatment as they can provide useful information about types of foods and exercises that can be done to help with dysphagia.
Recommended bibliography:
- Belafsky, Peter C., et al. "Validity and reliability of the Eating Assessment Tool (EAT-10)." Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology 117.12 (2008): 919-924.
- Clavé Civit P, García Peris P. Guide to diagnosis and nutritional and rehabilitative treatment of oropharyngeal dysphagia. Ed. Glosa, 2011